By David Jacobson, Temblor

In California, when most people think about faults, their thoughts are immediately drawn to the San Andreas, and to a lesser extent, the Hayward Fault. However, in Northern California, there is almost no seismicity on the San Andreas. Instead, the majority of the earthquakes occur on faults that are parallel to and east of the San Andreas. These faults are part of the greater San Andreas system, and are capable of generating large magnitude earthquakes. Today, we thought we’d take a look at two of them.
The Maacama and Bartlett Spring faults lie approximately 50 km and 80 km east of the San Andreas respectively. All of these faults are members of the greater transform boundary between the Pacific and North American plates, a margin primarily composed of nearly pure right-lateral strike-slip faults. Both the Maacama and Bartlett Springs faults are known to be active based on seismicity and creep. Creep implies there is very slow, relatively continuous motion on a fault due to tectonic deformation. While faults that creep tend to not rupture in large earthquakes, the Hayward Fault running through the San Francisco East Bay creeps and has ruptured in M=7+ quakes. So, it is not a black and white rule.
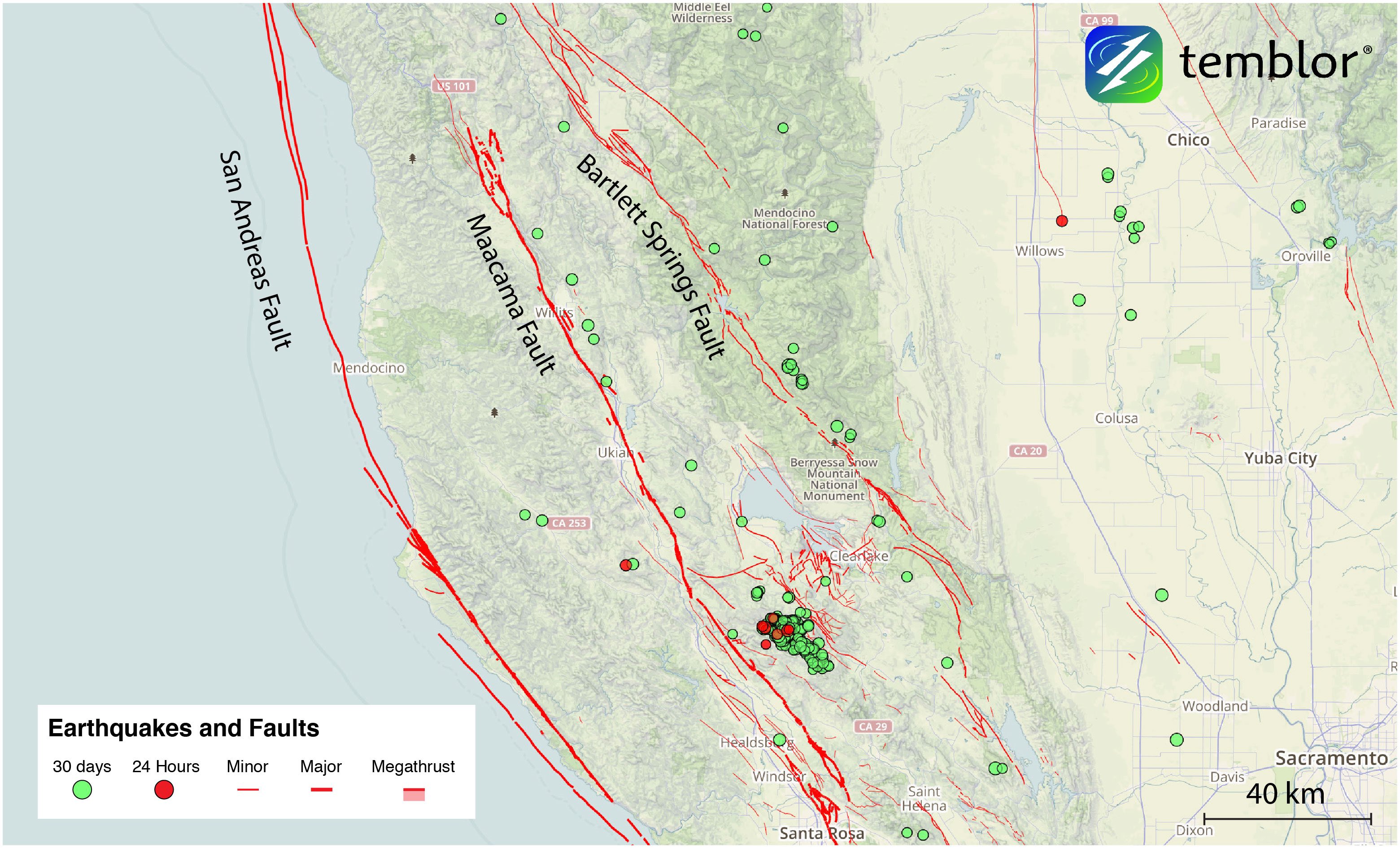
What is evident from the Temblor map above is that within the last month, there has been microseismicity along both the Maacama and Bartlett Springs faults. By examining the USGS database, it was determined that the seismicity in the last month is relatively consistent with previous months. While almost none of these quakes were felt, they highlight an obvious difference with the San Andreas. In the last month, there have been no M=1+ earthquakes on the northern San Andreas Fault. In fact, the portion of the San Andreas that ruptured in the 1906 earthquake (From San Juan Bautista to the Mendocino Triple Junction) shows almost no signs of seismic activity. What this shows that if we only used seismicity to identify faults, we would miss the greatest threat Northern California faces.
While the San Andreas may be capable of producing larger earthquakes than either the Maacama or Bartlett Spring faults, quakes on both of these could be very damaging. Based on their relative lengths, M=7.5 earthquakes are possible on either the Maacama or Bartlett Springs faults. Such quake could be devastating to the city of Ukiah, which sits right on the Maacama Fault. Based on the Global Earthquake Activity Rate model, which is available in Temblor, the likely earthquake in your lifetime for this part of California is M=6.25+. This model uses global strain rates and seismicity since 1977 to forecast future events. What this suggests is that a M=7.5 earthquake would be a unique event, but nonetheless possible.
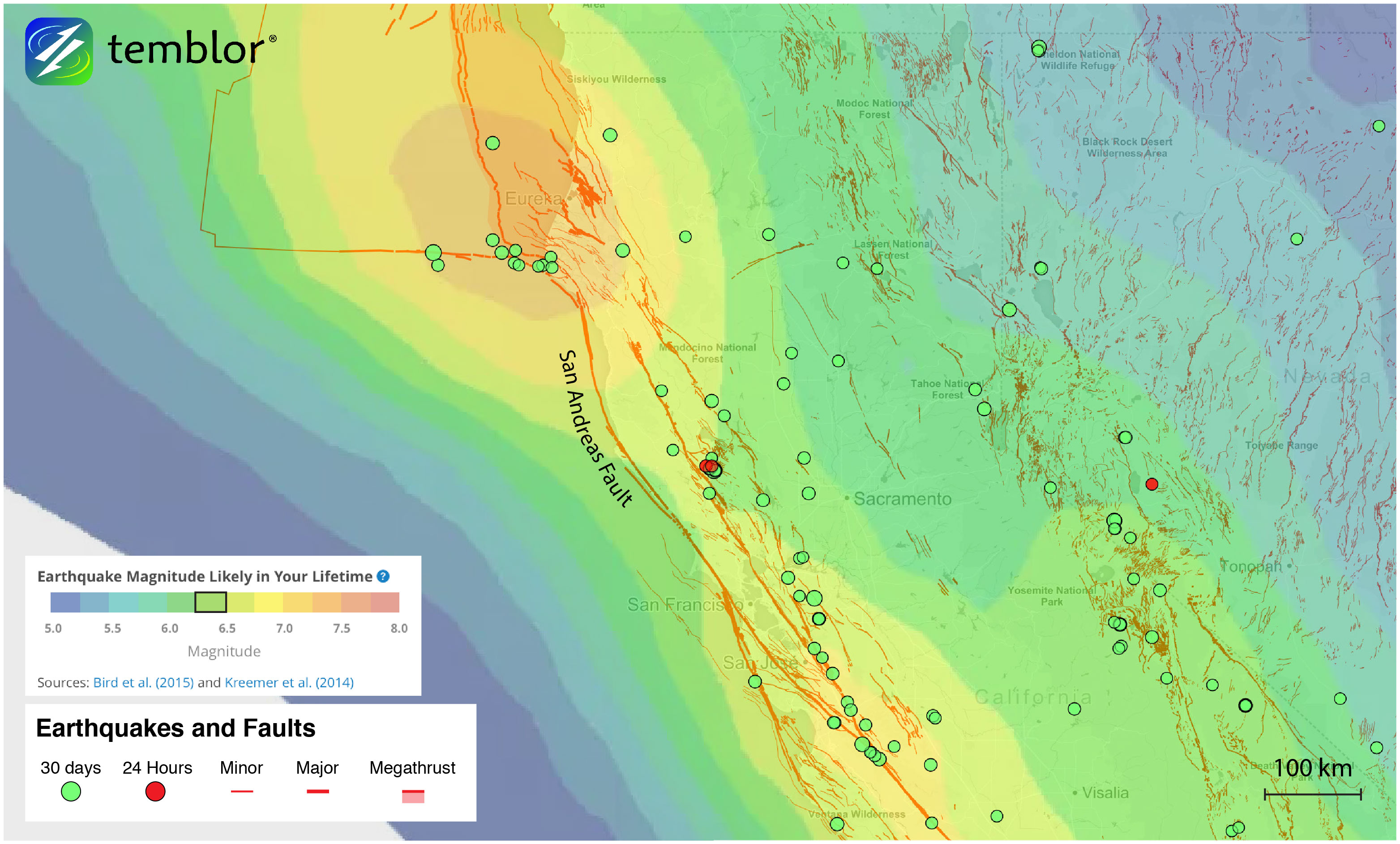
The Maacama Fault also deserves a bit of extra attention because at its southernmost extent in Santa Rosa, there is a stepover with the Rodgers Creek Fault. Because of their close proximity, it is possible that an earthquake originating on the Rodgers Creek Fault, could rupture onto the Maacama Fault, or vice versa. This has serious implications for the city of Santa Rosa, which suffered heavy damage in the 1906 earthquake (see below). What all of this indicates is that while the San Andreas may get all the publicity, Northern California has many other large faults capable of generating large earthquakes.

References
USGS
Ohlin, H.N., McLaughlin, R.J., Moring, B.C., and Sawyer, T.L., 2010, Geologic map of the Bartlett Springs Fault Zone in the vicinity of Lake Pillsbury and adjacent areas of Mendocino, Lake, and Glenn Counties, California: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2010–1301, scale 1:30,000. (Available at https://pubs.usgs.gov/sim/3125/.)
Robert J. McLaughlin, Andrei M. Sarna-Wojcicki, David L. Wagner, Robert J. Fleck, V.E. Langenheim, Robert C. Jachens, Kevin Clahan, and James R. Allen, Evolution of the Rodgers Creek–Maacama right-lateral fault system and associated basins east of the northward-migrating Mendocino Triple Junction, northern California, 2012, Geosphere, Vol. 8, Issue 2, DOI:10.1130/GES00682.1
- Earthquake science illuminates landslide behavior - June 13, 2025
- Destruction and Transformation: Lessons learned from the 2015 Gorkha, Nepal, earthquake - April 25, 2025
- Knock, knock, knocking on your door – the Julian earthquake in southern California issues reminder to be prepared - April 24, 2025
